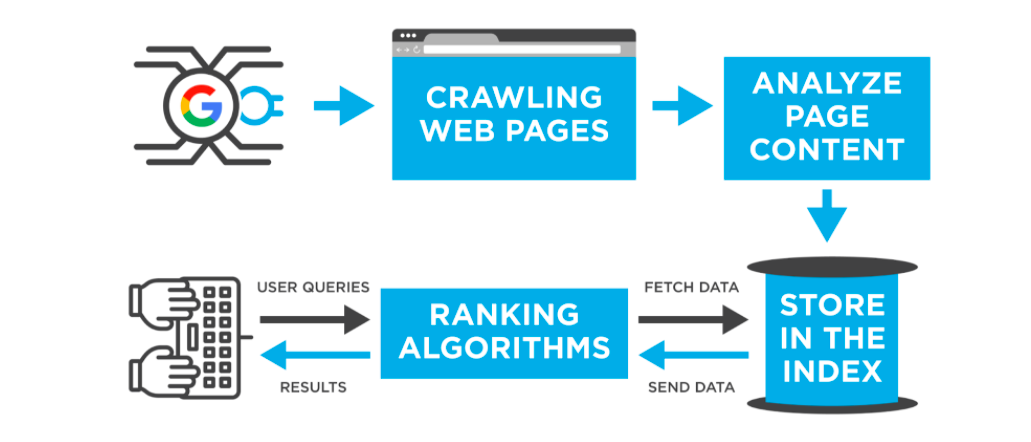
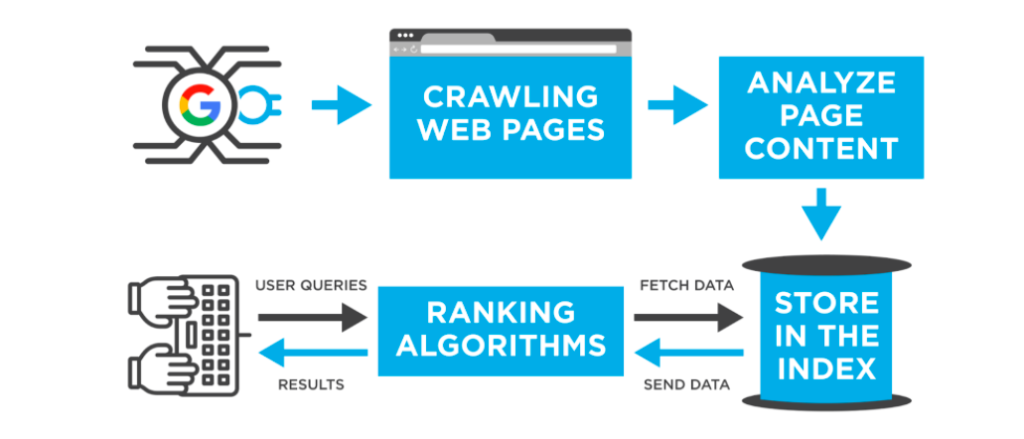
Ever wondered how search engines work their magic and deliver the most relevant results to your queries? Well, the inner workings of these digital wizards might seem complex, but fear not! In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how search engines operate behind the scenes, uncovering the fascinating algorithms and intricate processes that allow them to sift through millions of web pages and present you with the information you seek. So, get ready to embark on an enlightening journey as we demystify the inner workings of search engines!
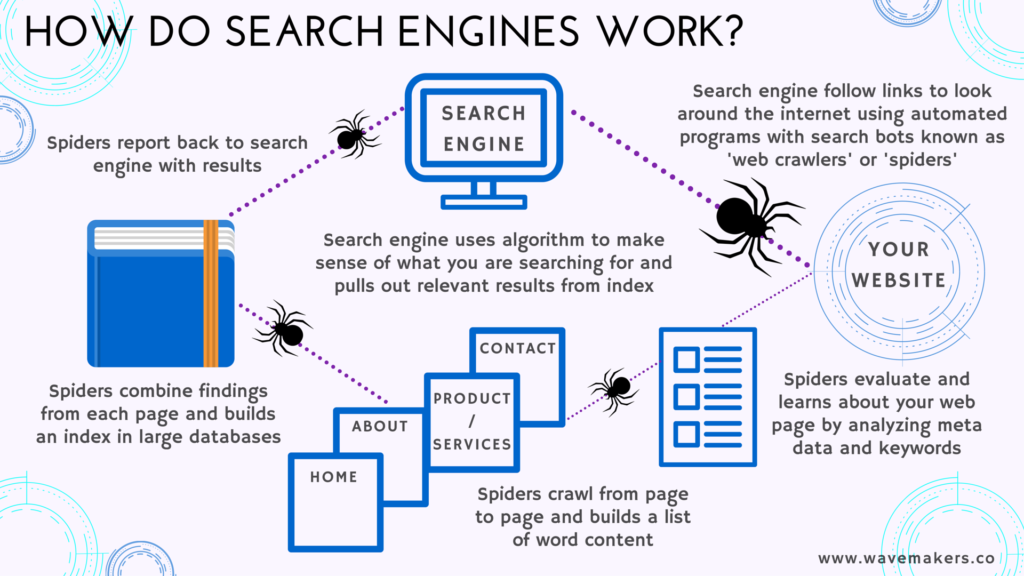
This image is property of wavemakers.co.
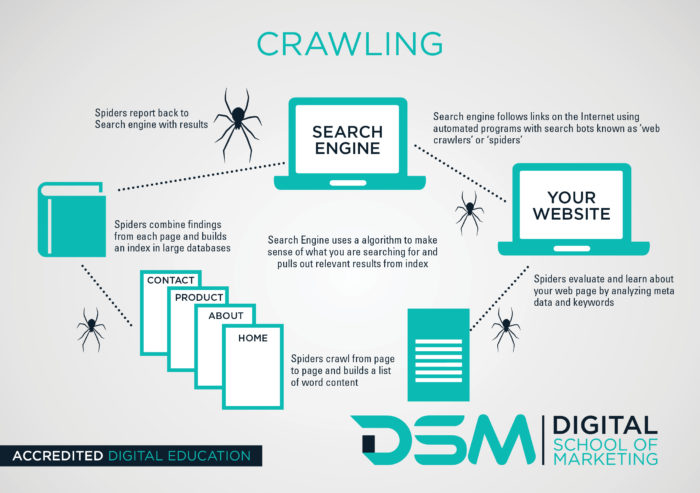
Crawling
What is crawling?
Crawling is the process by which search engines discover and index web pages. It involves systematically going through the entire internet, following links from one page to another, and collecting information about each page it encounters. By crawling the web, search engines build an index of all the pages they find, which allows them to provide relevant search results to users.
How do search engines crawl the web?
Search engines use automated programs called spiders or bots to crawl the web. These bots start with a list of known URLs, such as popular websites or sitemaps submitted by website owners. From there, they follow the links on those pages to discover new URLs, and continue the process recursively. This allows search engines to uncover new pages and update their index with fresh information.
Crawling challenges
Crawling the web presents various challenges for search engines. One challenge is the sheer size of the internet, with billions of web pages constantly being added, modified, or removed. Search engines need to ensure they crawl as much of the web as possible, while also being mindful of their resources and the time it takes to crawl each page.
Another challenge is dealing with duplicate content. Search engines need to identify and handle duplicate pages effectively to avoid indexing multiple copies of the same content. They also need to navigate through websites with complex structures or with blocked sections, such as password-protected pages or those requiring specific user interactions.
Crawling frequency
Search engines determine how often they crawl each website based on factors like the website’s authority, update frequency, and the historical reliability of its content. More authoritative and frequently updated sites are crawled more often, while lesser-known sites with fewer updates might be crawled less frequently. However, search engines adjust their crawling frequency dynamically based on various factors to ensure they provide the most up-to-date information in their index.
Indexing
What is indexing?
Indexing is the process of organizing and storing the information collected during the crawling phase. Once a search engine’s bots crawl a web page, they extract various elements like the page’s content, title, meta tags, and links. This extracted information is then analyzed and added to the search engine’s index, a massive database that catalogs the contents of all web pages.
How do search engines index web pages?
When search engine bots crawl a web page, they explore its HTML structure to understand its different elements. They index the page’s content, including the text, images, and videos, and analyze the relevance and quality of the information. Additionally, they consider other factors like the website’s overall authority, the presence of backlinks, and the user experience it provides.
Indexing challenges
One challenge search engines face during the indexing process is correctly understanding and categorizing the content of web pages. Bots rely on algorithms to determine the purpose and relevance of each page, but they may sometimes misinterpret the content or fail to recognize its context, leading to inaccurate indexing.
Another challenge is dealing with dynamically generated or personalized content. Websites often display different content to different users based on their location, preferences, or past behavior. Search engines strive to index the most relevant version of a page, but it can be challenging to account for and index all possible variations accurately.
Indexing scale
Search engines aim to index a vast number of web pages to provide comprehensive and extensive search results. The scale of indexing is immense, with billions of web pages being indexed by top search engines. To handle such a massive amount of data, search engines employ powerful servers and infrastructure, as well as efficient algorithms for indexing and retrieving information quickly.

This image is property of www.devopsschool.com.
Ranking
What is ranking?
Ranking is the process of determining the order in which search engine results are displayed for a given search query. When a user submits a search query, the search engine’s ranking algorithms analyze the indexed pages and determine their relevance and quality to the query. The search engine then ranks the pages, listing the most relevant and useful ones at the top of the search results page.
How do search engines determine rankings?
Search engines use complex ranking algorithms to evaluate the relevance and quality of web pages. These algorithms consider numerous factors, including keyword relevance, website authority, user engagement metrics, and the page’s overall user experience. By analyzing these factors, search engines attempt to provide the most accurate and helpful results for each search query.
Ranking algorithms
Search engine ranking algorithms are proprietary and constantly evolving. Each search engine has its own unique algorithm, often consisting of hundreds of different ranking signals and machine learning models. These algorithms continuously learn and adapt based on user behavior, feedback, and advancements in technology to improve the accuracy and quality of search results.
Factors affecting rankings
Several factors influence the rankings of web pages in search results. Keyword relevance plays a significant role, as search engines look for pages that contain the relevant keywords in the page’s content, title, headings, and meta tags. Backlinks and social signals also impact rankings since they indicate the popularity and authority of a page.
The user experience is another crucial factor. Search engines aim to rank pages that provide a positive user experience, including fast loading times, easy navigation, and mobile-friendliness. Additionally, the quality and depth of the content, as well as its originality and usefulness to users, are important factors in determining rankings.
Relevance
Relevance in search engines
Relevance is a fundamental concept in search engines as it directly affects the quality of search results. When users enter a search query, they expect the search engine to provide them with relevant information that matches their intent. Search engines analyze the keywords and context of the search query to understand user intent and deliver the most relevant results.
Importance of keywords
Keywords play a crucial role in determining the relevance of a web page to a search query. Search engines look for pages that contain the relevant keywords in their content, titles, headings, and other elements. However, search engines have evolved beyond simple keyword matching and now consider the overall context, user intent, and the semantic meaning of the search query to provide more accurate results.
It is essential for website owners and content creators to conduct keyword research to understand the terms and phrases users commonly search for. By optimizing their content with relevant keywords, they can increase the chances of their pages ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and reaching the right audience.
Understanding user intent
Understanding user intent is a major focus for search engines. They aim to deliver results that match the user’s underlying reason for performing a search. By analyzing the keywords, context, and past search behavior, search engines can infer the intent behind a search query and provide results that are most likely to satisfy the user’s needs or desires.
To improve the relevance of their search results, search engines use sophisticated natural language processing techniques, machine learning models, and user feedback. These methods help them understand and interpret the meaning behind search queries and deliver results that go beyond exact keyword matching.
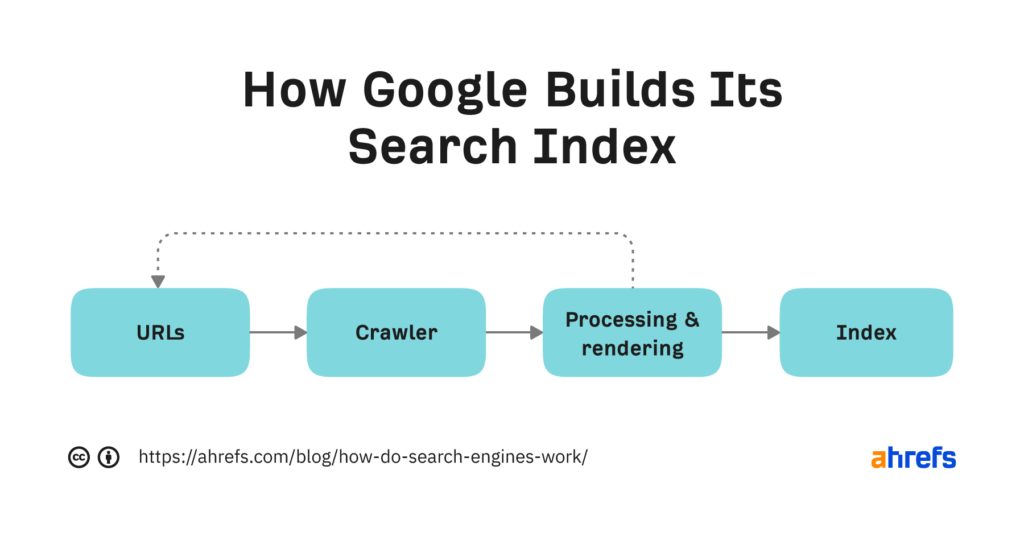
This image is property of ahrefs.com.
Search Queries
What are search queries?
Search queries are the words or phrases that users enter into search engines when looking for information or resources on the internet. They typically consist of one or more keywords that describe the user’s desired information or the problem they are trying to solve. Search queries are the initial interaction point between users and search engines and play a vital role in retrieving relevant search results.
Types of search queries
Search queries can be classified into different types based on user intent and the nature of the search. Some common types of search queries include:
-
Informational queries: These are queries where users are seeking information about a particular topic, such as “what is the capital of France?” or “how does solar energy work?”
-
Navigational queries: These queries are used when users are looking for a specific website or web page. For example, a user might search for “Facebook” instead of directly typing the URL in the browser.
-
Transactional queries: Transactional queries indicate that the user has the intention to perform a specific action or transaction, such as buying a product or booking a service. Examples include “buy iPhone X” or “book a hotel in New York.”
-
Commercial investigation queries: These queries arise when users are in the research phase of making a purchase decision. They seek information about different options, comparisons, or reviews. For instance, a user might search for “best DSLR cameras” or “iPhone vs. Samsung comparison.”
-
Local queries: Local queries are related to location-specific information or businesses. Users search for services, products, or attractions in a particular area, such as “Chinese restaurant in London” or “dentist near me.”
Query understanding and matching
Search engines employ complex algorithms to understand and match search queries with the most relevant web pages. They consider factors like keyword relevance, user location, search history, and user behavior to improve the accuracy of search results.
Query understanding involves analyzing the keywords and context of the search query to determine the user’s intent and what type of information they are looking for. Search engines also consider the user’s location and other personalization factors to provide results that are tailored to their specific needs.
Once the search engine understands the query, it matches it with indexed pages that are most likely to satisfy the user’s intent. The ranking algorithms then determine the order in which the matched pages are displayed in the search results, considering factors like relevancy, quality, and user experience.
User Experience
Importance of user experience
User experience (UX) plays a crucial role in search engine optimization and the overall success of a website. Search engines aim to provide the best possible results to users, and a positive user experience is a key determinant of a website’s ranking.
A good user experience involves factors like easy navigation, fast loading times, engaging content, and mobile-friendliness. When users have a positive experience interacting with a website, they are more likely to stay longer, explore more pages, and potentially convert into customers or loyal visitors. Search engines take these user behavior signals into account when evaluating the quality and relevance of a website.
Mobile-friendliness and responsiveness
In today’s mobile-centric world, having a mobile-friendly website is essential. With the increasing number of users accessing the internet through mobile devices, search engines prioritize websites that are optimized for mobile browsers. Mobile-friendly websites adapt their layout and design to different screen sizes, ensuring a seamless user experience across devices.
Website responsiveness is closely related to mobile-friendliness. Responsive design allows websites to automatically adjust their layout and content based on the device and screen size, providing an optimal viewing experience. Websites that are not optimized for mobile devices may suffer in search engine rankings and lose potential visitors.
Page load speed
Page load speed is another critical aspect of user experience. Slow-loading websites frustrate users and can lead to high bounce rates, where users leave the website without engagement. Search engines recognize the negative impact of slow-loading pages on user experience and consider page load speed as a ranking factor.
To improve page load speed, website owners can optimize their code, compress images, use caching techniques, and choose reliable hosting providers. Faster websites not only provide a better user experience but also contribute to higher search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
This image is property of jellymarketing.ca.
Updates and Changes
Search engine updates
Search engines frequently update their algorithms and processes to improve the quality of search results and provide a better user experience. These updates can range from small tweaks to major algorithm changes, with the goal of delivering more relevant, reliable, and useful information.
Updates may focus on addressing specific issues like combating spam, reducing the visibility of low-quality content, or enhancing the understanding of user intent. Search engine updates are often accompanied by guidelines and best practices for website owners and SEO professionals to ensure their websites comply with the latest standards and maximize their visibility in search results.
Algorithm changes
Algorithm changes are an integral part of search engine updates. Search engine algorithms are the complex mathematical formulas used to determine the relevance and ranking of web pages. Algorithm changes can impact how websites are ranked, potentially leading to shifts in search engine rankings.
Search engines like Google often roll out algorithm updates, such as Google Panda, Google Penguin, and Google Hummingbird, to refine their ranking methodology. These updates aim to reward high-quality content, penalize manipulative tactics, and provide users with the most relevant and trustworthy information.
Adapting to user behavior
Search engines constantly adapt to changes in user behavior to provide the best search experience. With advancements in technology and shifts in user preferences, search engines need to understand and adapt to how users interact with the internet.
For example, the rise of voice search has prompted search engines to refine their algorithms to better understand spoken queries and deliver voice-friendly search results. Similarly, the increased use of mobile devices has led to a focus on mobile-friendliness and mobile-first indexing.
By staying responsive to user behavior and preferences, search engines can continue to offer a search experience that meets the evolving needs of users.
Search Engine Optimization
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving a website’s visibility and rankings in search engine results. It involves various strategies, techniques, and optimizations to make a website more relevant, trustworthy, and user-friendly. The goal of SEO is to drive organic (non-paid) traffic to a website and increase its visibility to potential visitors.
Importance of SEO
SEO is essential for website owners and businesses looking to attract organic traffic and increase their online presence. By implementing effective SEO strategies, websites can improve their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs), enhance their user experience, and reach a wider audience.
Proper SEO helps search engines understand the content and purpose of a website, making it easier for them to index and rank the site. Websites that invest in SEO techniques are more likely to appear prominently in search results and attract quality traffic from users actively seeking relevant information or products.
On-page SEO techniques
On-page SEO refers to optimizations made directly on a website to improve its visibility and search engine rankings. It involves optimizing various elements of a web page, including:
-
Title tags: Each page should have a unique and descriptive title tag that accurately summarizes the content.
-
Meta descriptions: Meta descriptions provide brief summaries of page content in search engine results. Optimized meta descriptions increase click-through rates.
-
Heading tags: Properly structured heading tags (H1, H2, etc.) help search engines understand the hierarchy and importance of content on a page.
-
URL structure: Using descriptive and keyword-rich URLs makes it easier for search engines and users to understand the relevance of a page.
-
Keyword optimization: Strategic use of relevant keywords throughout the content helps search engines associate the page with specific search queries.
-
Image optimization: Optimizing images with descriptive filenames and alt text improves accessibility and helps search engines understand the visual content.
Off-page SEO techniques
Off-page SEO refers to optimizations made outside of the website itself to improve its visibility and authority. Key off-page SEO techniques include:
-
Link building: Acquiring backlinks from reputable and relevant websites helps search engines determine a website’s authority and relevance.
-
Social media engagement: Actively engaging with and sharing content on social media platforms can increase brand visibility and generate organic traffic.
-
Online directories and citations: Listing a website in relevant online directories and obtaining citations from reputable sources can enhance the website’s online presence.
-
Guest blogging: Publishing high-quality content as a guest author on other websites can increase brand exposure and generate valuable backlinks.
-
Influencer outreach: Collaborating with influencers or authoritative figures in the industry can help raise brand awareness and attract organic traffic.
Implementing a combination of on-page and off-page SEO strategies is crucial for long-term success in search engine rankings.
This image is property of digitalschoolofmarketing.co.za.
Paid Search Results
What are paid search results?
Paid search results, also known as sponsored results or paid advertisements, are search engine results that are displayed prominently at the top or side of search engine results pages (SERPs). These results are usually marked as ads and are separate from the organic search results.
Pay-per-click advertising
Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising is the most common method of paid search advertising. With PPC, advertisers bid on specific keywords or key phrases related to their products or services. When a user enters a search query containing those keywords, the search engine displays the advertiser’s ad, typically above the organic search results.
Advertisers only pay when a user clicks on their ad, hence the name pay-per-click. PPC advertising allows advertisers to target specific keywords and demographics, set budgets, and track the performance of their ads.
Paid search vs. organic search
Paid search and organic search are two distinct types of search results. Organic search results are the non-paid listings generated by search engine algorithms based on relevance and authority. They rely on solid SEO practices, website quality, and content relevancy to appear prominently in search engine results.
Paid search results, on the other hand, are the ads that advertisers directly pay for to appear at the top or side of search engine results. They provide immediate visibility and can help bypass the time and effort required for organic search rankings.
Both paid search and organic search have their benefits. Paid search offers instant visibility and the ability to target specific keywords and demographics. Organic search, although it requires longer-term efforts, can provide sustained visibility and generate organic traffic without direct advertising costs.
Search Engine Monetization
Revenue generation for search engines
Search engines generate revenue through various monetization methods. The primary source of revenue for search engines is advertising, particularly pay-per-click (PPC) advertising. Advertisers bid on keywords, and search engines display their ads when relevant searches are performed. The search engines earn money when users click on these ads.
Additionally, search engines may offer advertising platforms, such as Google Ads, that enable advertisers to create, manage, and optimize their ad campaigns. These platforms provide detailed targeting options, performance metrics, and customizable ad formats for advertisers to reach their desired audience effectively.
Search engines may also generate revenue through partnerships, such as affiliate marketing programs, where they receive a commission for promoting products or services on their platforms.
Advertising platforms and models
Search engine advertising platforms, like Google Ads, offer various advertising models for businesses to choose from:
-
Cost Per Click (CPC): Advertisers pay a predetermined amount each time a user clicks on their ad. This model is commonly used in pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns.
-
Cost Per Impression (CPM): Advertisers pay a fixed rate for every 1,000 ad impressions, regardless of whether users click on the ads. CPM is often used for brand awareness campaigns.
-
Cost Per Action (CPA): Advertisers pay only when a specific action is taken, such as a form submission, purchase, or sign-up. CPA models are used to measure and optimize conversion rates.
Search engines provide advertisers with a range of targeting options, including specific keywords, demographics, geographic location, and browsing behavior. These targeting capabilities help advertisers reach their intended audience effectively and maximize their return on investment (ROI).
In conclusion, search engines work through a complex process that involves crawling the web, indexing web pages, ranking them based on relevance, and providing users with highly accurate search results. Understanding how search engines work and optimizing websites accordingly can greatly improve visibility, traffic, and overall success on the internet.