Imagine a world where every website, app, and digital product is designed with the utmost thought and consideration for your needs and preferences. A world where every interaction you have with technology is seamless, intuitive, and enjoyable. This is precisely what User Experience Design aims to achieve. By placing the user at the center of the design process, User Experience Design creates digital experiences that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and user-friendly.
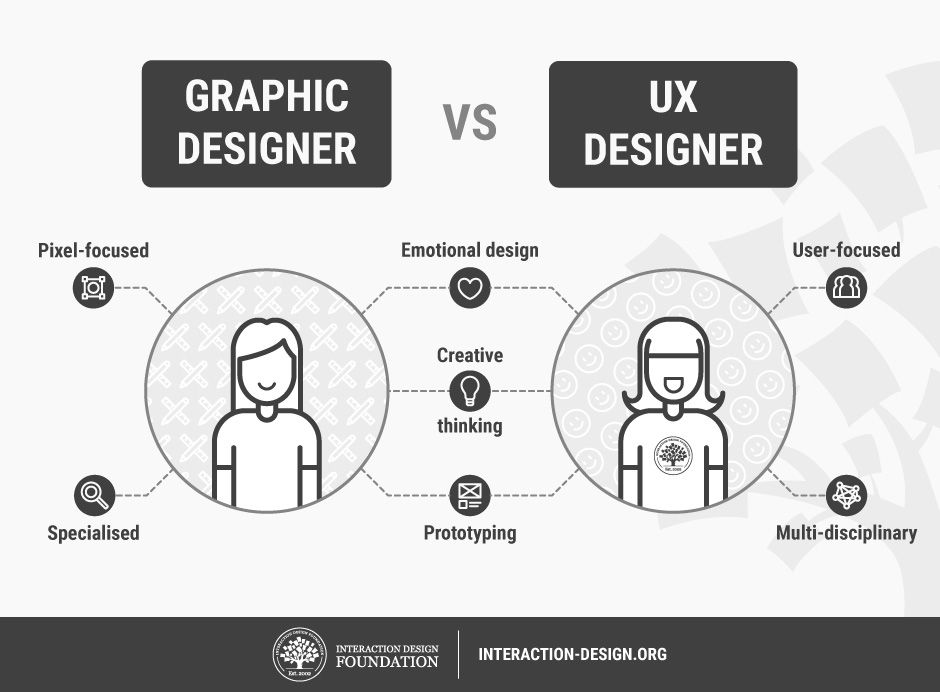
This image is property of public-media.interaction-design.org.
Importance of User Experience Design
User experience design plays a crucial role in creating a positive and satisfying interaction between users and digital products or services. By placing the user at the center of the design process, user experience design aims to understand their needs, behaviors, and motivations, and then create a seamless and enjoyable experience to meet those needs. This focus on the user ultimately leads to enhanced user satisfaction, increased conversion rates, and improved user retention.
Enhancing User Satisfaction
User satisfaction is at the core of a successful user experience design. When users have a positive experience with a product or service, they are more likely to feel satisfied and develop a sense of loyalty towards the brand. By understanding the user’s needs, preferences, and pain points, user experience designers can create intuitive interfaces, clear communication, and easy navigation, resulting in a seamless experience that exceeds user expectations and leaves them feeling satisfied.
Boosting Conversion Rates
Conversion rates refer to the percentage of users who take the desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a form. User experience design can significantly impact conversion rates by optimizing the user journey and removing any barriers that might deter users from completing the desired action. By focusing on creating a smooth and intuitive flow, providing clear calls to action, and addressing potential user concerns, user experience designers can boost conversion rates and drive more successful outcomes.
Increasing User Retention
User retention refers to the ability to keep users engaged and coming back to a product or service over time. A positive user experience is a key factor in achieving high user retention rates. When users find value in a product or service and have a pleasant experience using it, they are more likely to continue using it, refer it to others, and become loyal customers. By continuously improving the user experience and addressing user feedback, user experience design helps to foster long-term user engagement and increase user retention rates.
Key Principles of User Experience Design
To create effective user experiences, designers follow key principles that guide their design decisions. These principles focus on putting the user first and ensuring that the design is clear, consistent, and easy to understand.
User-Centric Design
User-centric design is the foundational principle of user experience design. It involves understanding the target users, their needs, motivations, and goals, and designing with their preferences in mind. By empathizing with the users, designers can create products and services that truly meet their needs and provide a positive experience.
Clear and Consistent Communication
Clear and consistent communication is vital for a successful user experience. Users should be able to understand how to use a product or service without confusion. User experience design focuses on providing clear instructions, labeling, and feedback, ensuring that users can easily understand the system and navigate through it effectively.
Simplicity and Minimalism
Simplicity and minimalism are key principles in user experience design. By keeping the design simple and eliminating unnecessary complexities, designers can create a clean and intuitive interface. A minimalist approach helps to remove distractions and allows users to focus on the essential elements, improving their overall experience and reducing cognitive load.

This image is property of miro.medium.com.
The User Experience Design Process
User experience design follows a systematic approach to ensure that the end product meets the needs and expectations of the users. This process involves several stages, including user research, information architecture, and interaction design.
User Research
User research is a vital first step in the user experience design process. It involves gathering insights about the target users, their behaviors, and their preferences. This research can be conducted through various methods, such as interviews, surveys, observations, and user testing. By understanding the users’ needs and motivations, designers can make informed design decisions that align with user expectations.
Information Architecture
Information architecture focuses on organizing the content and functionality of a product or service in a way that is intuitive and easy to navigate. This involves creating a clear and logical structure, labeling content effectively, and developing a hierarchy that guides users through the interface. Information architecture helps users find what they need quickly and easily, improving the overall user experience.
Interaction Design
Interaction design focuses on designing the interactions between users and a product or service. It involves creating intuitive and meaningful interfaces that allow users to interact with the system effectively. Interaction designers use various techniques, such as creating interactive prototypes and conducting usability testing, to refine and improve the interactions and ensure a seamless user experience.
User Research
User research is a crucial phase in the user experience design process as it provides valuable insights into the target users and their needs. It involves gathering and analyzing information about the users’ behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
Defining User Personas
Defining user personas is a common method used in user research. User personas represent fictional characters that embody the characteristics, goals, and behaviors of the target users. By creating user personas, designers can have a better understanding of who they are designing for and tailor the user experience to meet their needs effectively.
Conducting Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product or service and collecting feedback on their experience. By conducting usability testing, designers can identify any usability issues, understand how users navigate through the interface, and gather valuable feedback for improvement.
Analyzing User Feedback
Analyzing user feedback is essential for refining the user experience. This feedback can be gathered through user interviews, surveys, or through user feedback channels within the product or service. By analyzing this feedback, designers can identify and address pain points, make iterative improvements, and ensure that the design meets the needs and expectations of the users.

This image is property of d3mm2s9r15iqcv.cloudfront.net.
Information Architecture
Information architecture focuses on organizing the content and functionality of a product or service. It aims to create a structure that is intuitive and easy to navigate, ensuring a positive user experience.
Organizing Content and Functionality
Organizing content and functionality involves categorizing information and features, and structuring them in a way that makes sense to the users. This includes grouping related content together, using meaningful labels, and creating a hierarchy that guides users through the interface. By organizing content effectively, users can find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
Creating Effective Navigation
Effective navigation is crucial for a seamless user experience. Navigation should be clear, intuitive, and provide easy access to all the important areas of the product or service. User experience designers use various navigation patterns and techniques, such as menus, breadcrumbs, and search functionality, to ensure that users can navigate through the interface with ease.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping are important tools in information architecture. Wireframes are low-fidelity designs that represent the basic layout and structure of a product or service. Prototypes, on the other hand, are more interactive and provide a closer representation of the final product. By creating wireframes and prototypes, designers can test and refine the information architecture, gather user feedback, and make iterative improvements.
Interaction Design
Interaction design focuses on designing the interactions between users and a product or service. It aims to create intuitive and meaningful interfaces that allow users to accomplish their goals efficiently and effectively.
Designing Intuitive User Interfaces
Designing intuitive user interfaces involves creating interfaces that users can understand and interact with easily. This includes using familiar patterns and conventions, providing clear visual cues, and minimizing the learning curve. By designing intuitive interfaces, user experience designers empower users to accomplish their desired tasks without frustration or confusion.
Developing Meaningful Interactions
Meaningful interactions refer to the interactions that provide value and contribute to the overall user experience. This can include interactive elements, animations, transitions, and feedback mechanisms. By developing meaningful interactions, designers engage users and create a more immersive and enjoyable experience.
Usability Testing and Iteration
Usability testing plays a vital role in interaction design. By observing users as they interact with the interface and collecting feedback, designers can identify any usability issues, understand how users navigate through the system, and make iterative improvements. Usability testing ensures that the interactions are efficient, effective, and aligned with user expectations.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Techniques for User Experience Design
Several techniques can be employed in user experience design to ensure a successful and satisfying user experience. These techniques include user journey mapping, wireframing and prototyping, and usability testing.
User Journey Mapping
User journey mapping is a visualization technique that represents the steps and touchpoints that a user goes through when interacting with a product or service. By mapping the user’s experience, designers can gain insights into the user’s emotions, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. User journey mapping helps designers understand the user’s perspective and create a seamless and satisfying experience.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping are essential techniques in user experience design. Wireframes are low-fidelity representations of the user interface, focusing on the structure and layout. Prototypes, on the other hand, provide a closer representation of the final product and allow for interactive testing. By creating wireframes and prototypes, designers and stakeholders can visualize and test the design, gather feedback, and make informed decisions.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product or service and collecting data on their experience. This technique helps designers identify usability issues, gather user feedback, and make iterative improvements. Usability testing can be conducted at various stages of the design process to ensure that the design meets the needs and expectations of the users.
User Journey Mapping
User journey mapping is a powerful technique used in user experience design to gain a deeper understanding of the user’s experience. It involves visualizing the steps and touchpoints that a user goes through when interacting with a product or service.
Mapping the User’s Experience
Mapping the user’s experience involves identifying the various stages that a user goes through, from their initial interaction with the product or service to the final outcome. This includes capturing their emotions, thoughts, and actions at each stage. By visualizing the user’s journey, designers can gain valuable insights into the factors that influence their experience and identify areas for improvement.
Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities
User journey mapping helps designers identify pain points, which are areas of friction or frustration for the user. By pinpointing these pain points, designers can address them and find solutions to improve the user experience. Additionally, user journey mapping also helps identify opportunities to enhance the user experience and create moments of delight or surprise for the user.
Creating Seamless Interactions
The ultimate goal of user journey mapping is to create a seamless and satisfying user experience. By understanding the user’s journey and their needs at each stage, designers can create interactions that are intuitive, efficient, and aligned with user expectations. User journey mapping helps ensure that the user’s experience is smooth, enjoyable, and encourages them to engage with the product or service.
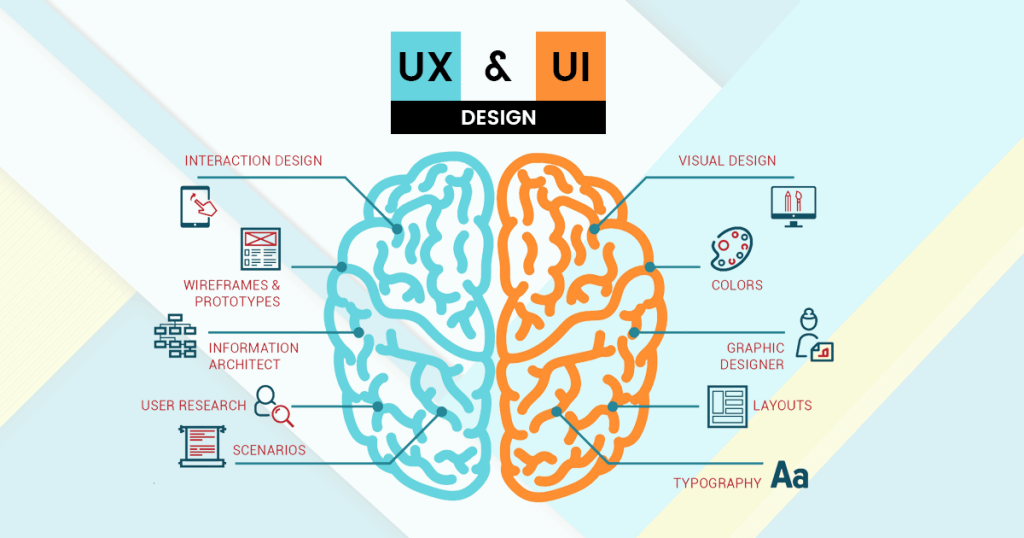
This image is property of miro.medium.com.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping are essential techniques used in user experience design to visualize and test the design before the final implementation.
Creating Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Wireframes are low-fidelity representations of the user interface, focusing on the structure and layout rather than the visual design. They provide a basic blueprint of the design and help designers and stakeholders visualize the layout, information hierarchy, and functionality. Creating low-fidelity wireframes allows designers to iterate quickly, gather feedback, and ensure that the design meets the user’s needs.
Refining and Testing Prototypes
Prototypes are more detailed representations of the user interface, providing a closer representation of the final product. They allow for interactive testing, giving users a realistic experience and enabling designers to gather feedback on the usability and functionality of the design. By refining and testing prototypes, designers can identify any issues or pain points, make iterative improvements, and ensure that the design meets the user’s expectations.
Iterating Based on User Feedback
User feedback plays a significant role in wireframing and prototyping. By testing the design with users, designers can gather valuable feedback on the usability, ease of use, and overall user experience. This feedback helps identify any areas of improvement and guides the iterative design process. By iterating based on user feedback, designers can create a design that is intuitive, user-friendly, and aligned with user expectations.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a crucial technique in user experience design that involves observing users as they interact with a product or service and collecting data on their experience.
Setting Test Objectives and Tasks
To conduct usability testing effectively, it is essential to define clear test objectives and tasks. Test objectives help determine what specific aspects of the user experience will be evaluated, while tasks provide users with specific actions to perform. By setting clear objectives and tasks, designers can gather focused feedback and gather insights into the usability and effectiveness of the design.
Gathering and Analyzing User Data
During usability testing, designers observe users as they interact with the product or service and collect data on their behavior, thoughts, and emotions. This data can be gathered through methods such as observation, interviews, or surveys. Once the data is collected, it is analyzed to identify any usability issues, pain points, or areas for improvement. By analyzing user data, designers can gain valuable insights and make informed design decisions.
Making Iterative Improvements
Usability testing is an iterative process that involves making improvements based on user feedback. By identifying usability issues and pain points, designers can make targeted improvements to enhance the user experience. This can include adjusting the design layout, improving navigation, or providing clearer instructions. By making iterative improvements, designers can refine the design, address user concerns, and create a user experience that meets the expectations and needs of the users.
In conclusion, user experience design is of utmost importance for creating a positive and satisfying interaction between users and digital products or services. By enhancing user satisfaction, boosting conversion rates, and increasing user retention, user experience design has a significant impact on the success and effectiveness of a product or service. By following key principles such as user-centric design, clear and consistent communication, and simplicity and minimalism, designers can create intuitive and enjoyable experiences for users. Through the user experience design process, including user research, information architecture, and interaction design, designers can gather insights, organize content effectively, and create meaningful interactions. Techniques such as user journey mapping, wireframing and prototyping, and usability testing further enhance the design process, allowing for iterative improvements and a user-centered approach. Ultimately, by prioritizing user experience design, businesses can create products and services that meet the needs and expectations of their users, leading to improved satisfaction, increased conversion rates, and higher user retention.


