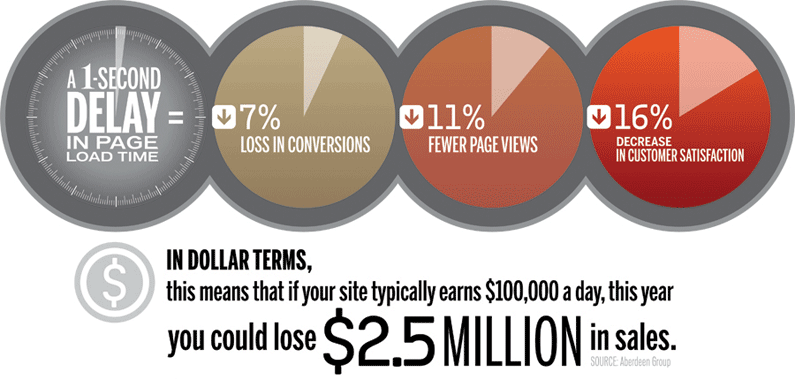
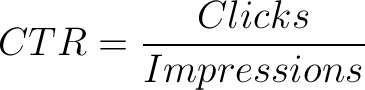Did you know that Google’s algorithm uses over 200 separate factors in order to rank websites?
If you are an automotive dealership trying to rank your website well, here are the top 200 ranking factors for automotive dealers that you need to know in order to get your website a great ranking in search results.
Buckle up—this is a long list, but all of this information will help you find a more successful rank for your website.
1. The age of your domain.
The age of your domain is important—it’s not the most important thing, but it still matters.
2. A keyword in your domain.
This used to be a very important ranking factor, now it is treated more as a sign of relevance to a searcher’s query.
Still important, and Google still bolds keywords in domain names when they show up in search results, but it’s not critical that you have a keyword in your domain name.
3. A keyword is the first word in your domain.
For example, if you had the keyword “car dealership New York” in your domain: “cardealershipNewYorksubaru.com,” you might get a boost in SEO.
A few years ago, you might have been given preference, and it is still important today—but it’s not nearly as important as other factors.
4. How long your domain has been registered.
The longer your domain has been registered, the more valuable it is considered—or rather, if your domain has been registered repeatedly for less than a year, that can hurt your SEO.
5. Keywords in subdomains.
Like keywords in domains, adding a keyword to your subdomain can boost your rank, but it isn’t strictly vital.
6. The history of your domain.
If someone else owned your domain before you and was either irresponsible with it or actively used black hat SEO methods, Google may “reset” your site, so that backlinks do not function properly.
7. Exact match domains.
Exact match domains were all the rage five years ago. Now, exact match domains will only help your automotive SEO if the domain is high-quality. Low quality domains will hurt you.
8. Is your WhoIs private or public?
If your WhoIs is private, Google may see that as you trying to hide something, even if you didn’t realize you had privacy turned on.
While this might not be bad in and of itself, it can be bad when coupled with other negative factors.
9. Penalties to the WhoIs owner.
If the one of the other websites the owner has control over has been penalized, Google will usually take care to check out the rest of that owner’s websites.
10. A country-specific extension.
Having a country-specific TLD extension like .cn or .ca only helps your automotive website rank in that particular country—it can hurt your ability to rank outside of that country.
11. Title tags with keywords.
Aside from the page’s actual content, there is no more important place to have a keyword than in the title tag.
12. The title tag starts with a keyword.
Websites that have a keyword toward the beginning of the title tag do usually rank higher than those that have keywords at the end.
13. Keyword in description tag.
The description tag is important to click-through rate, but it doesn’t do very much for improving page rank—some, just not very much.
14. Keywords in your second title or H1 tags.
Again, keywords in this tag can improve your rank, but they are mostly recognized now simply as indicators of relevancy, not necessarily as extremely important for SEO.
15. Content contains more keywords than any other phrase.
While not nearly as important as it once was, having a keyword phrase dominated document still helps boost page rank.
16. Length of your content.
The more content your webpage has, the better.
Longer content allows for more keywords and boosts relevancy signals.
Webpages with more content are preferred over pages with very short content.
17. Density of keywords.
Keyword density used to be one of the most important ranking factors.
Today, however, it has seriously waned in importance.
Keyword density is still used to determine whether or not a webpage is relevant to a search but too many keywords can harm your ranking.
18. Use of LSI keywords.
LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing keywords) simply mean that your website uses keywords that are similar, but not identical to the other keywords.
For example, “car” vs. “vehicle” or “truck.”
19. Using LSI keywords in website tags.
If a standard keyword seems too repetitive, using an LSI keyword as a replacement will still be helpful.
20. Page load speed.
Google is now putting a huge emphasis on how quickly your website loads.
21. Duplicated or copied content.
Duplicated content, whether it is original to the webpage, but simply in the same place more than once, or actually copied from another webpage, can seriously harm your ranking.
22. Rel=Canonical tagging.
If you use this tag, you may be able to get Google to become blind to duplicate content.
23. How quickly the page loads on Google Chrome.
This is actually considered a separate ranking factor than how quickly the page loads with HTML.
24. Are the images optimized?
Your images should be just as optimized as the written content—from file name to title to caption to description to alt text.
25. How recent was your update?
You might not see much reason to update your automotive website routinely—except that Google prefers websites with recent updates.
26. How massive the updates were.
The more changes you make, the fresher your website appears. Total rewriting is more of a change than just changing a few words.
27. Update history.
How often the website has been updated over its history (if it has routine updates or is only updated when information changes), affects your ranking.
28. How prominent the keyword is.
Having the keyword in the first 100 words of the page can boost page ranking.
29. Keywords in other heading tags.
While not strictly necessary, having keywords in any and all subheading tags can improve how relevant Google believes your website to be.
30. Keyword phrasing.
Exact match keywords in content will usually enable a page to rank higher than if the content is dominated by keywords that contain all the same words, but in a different order.
For example, “New York automotive dealers” may rank better than “automotive dealers in New York.”
31. The quality of your outbound links.
If your outbound links are to authoritative sites, they will lend you authority.
32. The theme of your outbound links.
Your outbound links should have a consistent theme—they should all be related to your industry to maintain relevancy.
33. Spelling and grammar.
The better the grammar and spelling are on your page, the higher-quality that page appears.
34. Is the content original?
While syndicated content can do just fine, original content does much better.
35. Interactive content.
If you have an interactive element to your dealership’s webpage, like a search tool to find a car or building one from scratch, this can boost your ranking.
36. How many outbound links you have.
Some outbound links are good.
Too many can hurt your ranking.
37. Multimedia on the site.
The more multimedia you include on your website, the higher in quality it will appear.
38. Internal linking.
How many internal links each page has can help Google determine relevance.
39. Quality internal links.
Linking to higher quality or more authoritative pages can help pages that have less authority or are considered lower quality.
40. Number of broken links.
How man broken links your webpage has tells Google how well-kept your website is.
41. Your content’s reading level.
Most pages that rank well on Google have an intermediate reading level.
Advanced reading level sites rank below basic reading level sites.
Why?
Because Google and its searchers prefer content that appeals to the common man, not to people who are already experts.
42. Links used by affiliates.
There’s nothing wrong with being an affiliate, but there’s also nothing these links will do for your ranking.
In fact, if you only have affiliate links and are lacking any quality content, they can be a detriment.
43. Errors.
Like broken links, Google sees errors as a very bad thing.
It takes them as a sign of subpar coding, which often means that the website itself is low quality.
44. The authority of the domain.
How much authority the domain has can help boost your page over a similar page, if all other factors match exactly.
45. Your page rank.
Your current page rank is actually a ranking factor… but Google says it isn’t now. 🙂
46. The length of your URL.
Longer URLs can hurt your page rank.
47. How close the page is to the homepage.
How close the ranking page is to your website’s home page can actually improve that page’s rank in search results.
48. Whether or not you have human editors.
While no one has confirmed whether or not Google really uses human editors as a ranking factor, many believe that they do.
49. The category of your page.
The category your page is filed under can help to improve how relevant Google believes that page to be.
If it is closely related to the category it is under, this can give that page a boost.
50. Tags in WordPress.
If your website is built on WordPress, the tags can improve your relevancy signal.
51. Keyword in your URL.
Having a keyword in your URL ensures that Google will see your page as relevant.
52. Categories in a URL string.
Having a clear path from the homepage to your page, so that all of the categories filter into the next in a meaningful way can improve how relevant Google sees your page to be.
53. Citing your sources.
If you take information from other sources, citing those sources can help improve your quality rating.
This gives your webpage more authority, which is always a good thing.
54. Numbered or bulleted lists.
This type of formatting makes your content easier to read, which makes it more useful for site visitors and Google likes websites that are useful for visitors.
55. The page’s place in the sitemap.
The higher priority the page is, the better ranking it will have.
56. Having too many outbound links.
Some outbound links are great, but if you have too many, your website may actually leak its rating.
57. Other keywords used.
If the page has other keywords that it ranks well for, that can help boost a page’s ranking with one particular keyword.
58. How old the page is.
While fresher content is better, the page itself should be old.
59. Is the layout user-friendly?
The more user-friendly your layout is, the more valuable your website appears.
60. Parked domains.
Updates in the last few years have seriously decreased the page rankings of any and all parked domains.
61. How useful the content is.
There is a difference between content that is useful and content that is quality.
Useful content will always be quality, but quality content might not always be useful.
62. Content is valuable.
Google wants to provide its searchers with content they will find valuable.
Additionally, they are killing rankings on websites that just provide affiliate links and no real value.
63. A great contact page.
A contact page makes your page look more legitimate, especially if the information listed on your contact page is the same as the information in your WhoIs.
64. How trusted your domain is.
The more links you have on authoritative sites, the more your domain will be trusted.
65. The structure of your site.
A site that has a logical makeup is supposed to be easier for Google to categorize.
66. Updates across the site.
While updating the content on the specific page you are trying to rank is important, how fresh the entire site is can be equally important.
67. How many pages your site has.
A large website is less likely to be pinned as an affiliate or shill site.
68. A sitemap.
Having a sitemap can also help Google catalog your site.
69. Consistent uptime.
If you take your site down for maintenance or often have issues with your server, this can hurt your ranking.
70. Where your server is located.
Google does discriminate by geographical location, especially if your dealership is trying to rank for a specific place in the country.
71. SSL Certificates.
You should have one—the safer your website is, the higher its rank will be.
72. TOS and Privacy clauses.
Including these pages ups your content and page numbers and makes your website more legitimate.
73. Duplicating your meta info.
Copying and pasting your meta data could hurt your ranking.
74. Breadcrumbs.
If your website makes it easy to track back to the site visitor’s starting page, this improves user friendliness.
75. Mobile website or responsive design.
Google favors websites that have a mobile version or have responsive design.
76. YouTube videos.
Google gives YouTube the best seat in the house when it comes to search results.
77. Site functionality.
If your website is easy to navigate, has a low bounce rate, and plenty of views, these will boost your rankings.
78. Google Analytics and Webmaster Tools.
Google likes to give a boost to website owners who rely on the free tools they provide.
79. Reviews and reputation.
Your online reputation has a serious effect on your site ranking. If your dealership has great reviews on websites like Yelp, it can improve your ranking. If you have negative reviews, it can hurt you.
80. The age of domains with your backlinks.
The age of the domain that hosts one of your backlinks can have an effect on your ranking.
81. How many different domains link to you.
The number of different websites that are hosting your link is one of the most important ranking factors of the bunch.
One or two is good.
Twenty-one is better!
82. Number of links with different IPs.
This suggests that you haven’t just set up your own websites to generate backlinks.
83. Your images have alt text.
Include a keyword and you’ll see a boost in rankings, and traffic.
84. Includes links from top level domains.
While not every SEO expert believes this, including links from .coms and .edus on your site can help to improve your site’s visibility.
This may not help every website, but these domains are more likely to be reputable websites than those with crazy names.
85. How many pages link to that page.
The total number of links to that specific page, even within your own website, is its own ranking factor.
86. Linking domain authority.
The page ranking of domains that refer back to your website can affect your ranking.
87. Linking page authority.
The page ranking of that specific page that refers back to yours will also affect your ranking.
88. Your competitor’s links.
If you have links on your competitor’s pages, this can be a serious boost to your rankings, especially if they are ranking for the same keywords.
89. How many times the referral page is shared socially.
How many times your page is shared socially can seriously affect how valuable that link is.
90. Links to competitors with bad histories.
If your link shows up on websites that have a negative history, this can leak away your website’s rankings.
91. Guest posting.
Guest posting is a great way to attract people to your webpage, but you want to refer people through a contextual link in the content, not with a link in the bio section of your post.
92. Linking back to a referring domain.
A link on your page back to a referring website’s homepage could improve your visibility.
93. Links classified as “Nofollow.”
This is one of the most widely discussed topics in SEO, with no definitive comment from Google as to whether or not they help your page rank.
They have said that they generally don’t follow these links, but that implies that sometimes they will follow them, under special circumstances.
No one quite knows what those circumstances are, however.
94. How many different types of links you have.
If you have lots of links that fall into one “type” (just blog comments or just links in forum signatures), Google often sees those links as spam and might not count them.
On the other hand, having a wide variety of links can boost rankings.
95. Text around your link that suggests you paid to place it there.
If the word “sponsored” shows up near your link, Google may downgrade the importance or relevance of that link.
96. Content links.
Links that are embedded into the context, rather than into a bio or attached at the end of the content are more valuable.
97. Too many 301 redirects.
If the visitor bounces through a string of redirects before landing on the page they want, this can seriously dilute your page ranking.
98. The anchor text used for a backlink.
Anchor text used to be a very important ranking factor.
Today, anchor text is still important, as long as it describes the page it links to.
99. Anchor text for internal links.
It’s extremely important to have very relevant and descriptive anchor text for your internal links, as this proves relevancy to Google.
100. Attributing link titles.
This is what shows up when you mouse over a link and can help Google determine relevancy of a link.
101. Country-specific referring domains.
If websites that link back to your website have country-specific domains, that could help you rank in that country.
This likely will not be very applicable to automotive dealerships, unless you have a dealership in Canada or another country.
102. Where the link is placed in the content.
The closer the link to the beginning of the content, the more weight it will be given—but only slightly more weight. Links anywhere in content are great, as long as they meet all of the other relevancy and value criteria.
103. Where a link within content is located.
Links in content are more valuable than links in any other part of the page, including the footer or somewhere on the sidebar.
104. Relevancy of linking domain.
Google will give more weight to links from domains that are in your same industry. If you can get your link on car maintenance or advice websites, for example, this will improve your chance of being visible in search engines compared with a link from a dental website.
105. Relevancy of linking page to your dealership.
The more closely related the linking page is to your dealership’s specific niche, the better that link will be for raising your webpage’s profile.
106. The text that surrounds your link.
Google is heavily concerned these days with relevancy and value.
They will scan the text around the link to determine whether or not its placement is actually relevant to that page.
The more relevant it is, the better that link will be.
107. Links to pages that have your keyword in the title.
If you are trying to rank for a keyword like “Best Kia dealership in New Jersey,” if you can find a webpage that has that keyword as its title and get your link on that webpage, you will be rewarded with more visibility.
108. Links with a positive link velocity.
Your links will be better for your webpage if they have positive velocity.
109. Links with negative velocity.
Links with negative velocity will hurt your page ranking.
110. Links on hub pages.
Hub pages are considered very high quality resources, especially if they are on the same topic as your webpage.
111. Links on authority websites.
If a website has an “authority” ranking, getting a link there allows you to benefit from that site’s authority.
112. Wikipedia sources.
If your webpage is linked as a Wikipedia source, this adds some legitimacy to the content on your page, even though these are technically nofollow links.
113. Co-occurrences.
The words that show up around your backlinks regularly are used by Google to determine the topic of your page.
114. How old the backlinks are.
The older the backlink is, the more power it has when it comes to boosting your rankings.
115. How realistic the linked websites appear to the search engine.
Google can tell the difference between a real website and a network that is set up just to promote a webpage.
How?
By measuring the interaction between site visitors and the content.
If you build a blog network to promote a page on your dealership’s page, Google won’t value links to that network as highly as links to real websites.
116. How natural your linking profile appears.
The more natural your links’ profile appears (how diversified it is and how “expected” each link is) can affect your dealership’s page ranking.
117. Excessive link exchanging.
Google specifically lists link exchanging (to an excessive degree) as one of the practices to avoid.
118. Links generated by users vs. site owners.
Google will differentiate between links on very authoritative, website-owner-owned blogs and extension blogs, e.g. the difference between a link on the official WordPress blog and a blog that is hosted by WordPress.
119. 301 redirects.
The more 301 redirects a link is passed through, the more juice it loses on the way.
120. Microformats.
Pages that have some microformats are more likely to have a higher ranking than pages without microformats.
Why?
Because these pages usually have a higher click through rating, because their search listing is more convincing.
121. Listed on the DMOZ.
While there is no definitive proof that Google gives more attention to sites that are DMOZ listed, many people believe that Google does rate these pages as more trustworthy than those that are not listed.
122. The TrustRank of a site that links to you.
This rating (even if you did not ask for the link or did not place the link there), can have an effect on your own rating.
123. How many outbound links a page has.
If a page that contains a link to your page has lots of outbound links, you will get less juice from it than if the page had only a few outbound links.
124. Links in forum profiles.
If you put a link to your dealership’s website in one of your car forum profiles, this could actually hurt your page ranking, since Google sees these links largely as spam, even if they are legitimate links.
125. How long the content is around your link.
If the content that contains a link to your page has more than 500 words, this will be much more valuable than your link inside a hundred words or less.
126. The quality rating of the content that contains your link.
The quality of the content that contains your link can also affect your dealership’s page ranking, since Google will always prefer high-quality content across the board, rather than low quality content.
127. How many links are on the entire site.
If a site links to your page more than once, Google will only count the link once.
128. Your click through rate.
If your click through rate for a particular keyword is high, you are likely to get a boost in your page rankings for that keyword.
129. Click through rate for all keywords.
Your click through rate for all keywords used on your website will factor into your page ranking for all of those keywords.
A high click through rate indicates a high user interaction rate, which Google likes.
130. Your bounce rate.
While not everyone is convinced that bounce rate affects your page ranking, Google probably uses this rate in order to determine whether or not a page is high quality.
Since high quality pages are likely to have a lower bounce rate, low quality pages are likely to have a high bounce rate.
131. Your website’s total traffic.
The amount of traffic that your website gets is likely used to determine how high quality your website is, and therefore how valuable it would be to searchers looking for a particular keyword.
132. How much repeat traffic your website obtains.
Luckily, most dealerships have plenty of repeat traffic as users are researching their options and trying to figure out which dealerships and which brands they want to buy from.
Google gives preference to these sites because they are considered more valuable.
133. Blocked sites.
Though Google no longer has this feature on Chrome, users who use other browsers who can block sites can mark a website, which may affect your rating.
134. Bookmarking.
Chrome collects information about how many of their users have bookmarked a specific page and Google may give a special boost to webpages that are bookmarked regularly, as this marks them as valuable.
135. Data from Google’s toolbar.
Google Toolbar tracks how quickly a page loads and whether or not it contains malware, as well as plenty of other information, which Google can then use to change or influence a page’s ranking.
136. How many comments a webpage has.
If there is the opportunity to leave comments on a page, like on a blog post, Google gives preference to pages that have lots of comments.
137. How long someone stays on your page.
Called “dwell time,” Google tracks how much time users, on average, spend on your page.
The longer they stay, the more likely you are to have a high quality website.
If you have a short dwell time, this usually means that your website is low quality.
138. Whether or not the query needs fresh content.
If the page rankings have remained static for too long, Google might mix in some new pages to provide some new options, especially if the original pages don’t seem to be meeting the searchers’ needs.
139. The query needs more options.
If one website or a few websites are dominating the top of the search results, Google may add in some other websites to give the results some variety.
140. How often a specific user visits your website.
In search results that are presented to a user who frequents your website, your pages may be given a ranking boost.
141. Influences from past user searches.
What a user often searches for or what they simply have searched for in the past can affect your page ranking in relevant searches.
142. Geo-specific results.
Luckily for dealerships, Google will give preference to local websites that answer a searcher’s needs, over national or non-local websites.
That means that if someone searches just for “car dealership” they are far more likely to find yours in their local town, than your competitor’s in the next town over.
143. Safe search.
This factor probably will not apply to your dealership, but just in case it does: whether or not someone uses safe search for Google can affect your page ranking if you have adult or inappropriate content on your page.
144. Google+ circle members.
Google+ users who have added you to their circles will see your pages higher in search rankings than other users.
145. DMCA Complaints.
This is why it is so important not to steal content from other websites.
Pages against which there are DMCA complaints will be down-rated or even removed from the rankings.
146. How diverse the domains are in a search results.
Recent updates are fabled to have added more domains to each page, so that one domain cannot dominate a search result by ranking highly with many similar pages.
147. Whether or not your page is shopping related.
Depending on what the searcher is shopping for, Google will show them different results.
148. Local search.
If your dealership has a Google+ Local page, these will often be stuck on top of the organic search rankings and are therefore more likely to be on the top of relevant search results.
149. Keywords that trigger the news box.
If you have a keyword that is likely to be used in recent news articles, those news articles will appear higher in search results than your page.
150. Short tail searches favor big brands.
Google gives preference to larger, more recognizable brands when a user searches something very generic. If a user, for example, just searches “car dealerships,” they are likely to list big brands before your actual dealership.
151. Shopping results.
If you have cars listed as products on your webpage, these can be pulled and listed in Google’s shopping results, which will show up before the organically ranked pages.
152. Image results.
Image results also show up before most of the organically ranked pages.
153. Easter Eggs in Google searches.
There are a number of keywords that turn Google into a game or give it a special effect or some other interesting change.
While these are fun, they can make it difficult for users looking for an actual webpage about that topic to find what they’re looking for.
These are known as Easter egg searches about car dealerships.
154. Brand-specific searches.
If someone is searching for a specific brand, for example, the brand of car your dealership sells, if you have only one brand on your lot, searching just for that brand may bring up several pages on that brand’s domain, instead of bringing up a variety of pages.
155. How many Tweets about your page.
How many Tweets there are about your page can affect your page ranking, as this is a powerful social signal.
156. Authority of accounts that tweet about you.
If you have a bunch of random Twitter users tweeting about you, that might not have a much pull as having one tweet from an influencer.
157. How many Facebook likes your dealership’s website has.
Though Facebook doesn’t really like Google to dabble in their private affairs, Google probably uses the number of likes as a weak indication of social relevance.
158. How many shares your content has.
Having content that is heavily shared across social media, especially Facebook, works like a backlink for your dealership.
159. The authority of the Facebook profiles that like and share you.
The more popular the people are that like and share you can have an effect on your website’s page, as this changes the value of your social signals.
160. Pinterest pins.
How many times your dealership or something from your blog has been pinned on Pinterest definitely affects page ranking.
161. Votes on social sharing sites like Reddit and Digg.
The number of votes (up-votes being more valuable than down-votes) are a social signal that Google takes into account.
162. How many times your content is +1’d.
While Google has said that their social media is not used as a ranking factor, they still must factor in your social signals from this venue to determine how valuable your content is.
163. Authority of those accounts.
The authority of those Google+ accounts can definitely affect your social signals, just like the authority of Twitter and Facebook profiles that interact with you.
164. Authorship.
While you used to be able to apply for “Authorship” through Google, it is likely that they look at the relevancy and consistency of your posts in order to determine how much of an authority you are about a topic, which can affect the ranking of the pages you own.
165. Relevancy in social signals.
Google will usually look at the content around your link in a social media post in order to determine if it is relevant.
166. How social signals increase your authority.
If social signals increase your dealership’s authority ranking, this can affect your page ranking.
167. Using branded anchor text.
This technique can increase your dealership’s page ranking.
168. Number of people looking specifically for you.
If there are a high number of people looking for your dealership by name, using Google, this is likely to boost your page ranking.
169. If you have a Facebook page with likes.
Having lots of likes is a sign that some consumers find you valuable, which Google takes as a good sign that you actually are.
170. Your dealership has a relevant Twitter profile with followers.
You can’t just have a Twitter profile, you need to have followers, as this indicates that your dealership is legitimate and Tweets valuable information.
171. Your dealership has a LinkedIn Company page.
Having this page signifies that your dealership is legitimate, since most legitimate companies have one of these pages.
172. Your employees are listed on LinkedIn.
If your dealership’s employees have their own profiles and your dealership is listed there, this cements your brand’s legitimacy.
173. How legitimate your social media accounts appear.
Social media accounts don’t just need a lot of followers, they also need a lot of interaction.
174. News sites have mentioned your brand.
If you issue a press release about opening a new branch or charity work or some other significant event and a news site, even a local news site reports it, this is a brand signal that can be very useful.
175. Brands are mentioned, but aren’t linked.
Even if another website simply mentions your brand, this can help to build your legitimacy.
176. RSS Subscribers.
Though this service is rarely used today, if you let people subscribe to your RSS feed, this can be an indication of popularity.
177. Your dealership is listed on Google+ Local Listing.
Showing Google that you are real by giving your dealership’s address can help your ranking.
178. You pay taxes.
Google may even look at whether or not your business is reported as paying taxes in recent years to determine whether or not you are legitimate.
179. The Panda Penalty.
Websites that have been hit with a Panda Penalty in the past (for low-quality content), will have much lower rankings than those that have not.
180. Links to bad parts of the internet.
Just like a city, the internet has some sketchy parts.
A link on your website to one of these parts of the web, like payday loan websites, can hurt your visibility.
181. Being sneaky about redirects.
Google doesn’t like anything underhanded. If you are trying to use redirects to snatch visitors, Google will probably remove your site from rankings altogether.
182. Popups and other horrible ads.
If the advertisements on your website are annoying, Google see this as a low-quality website and will probably punish you for it.
183. Too much optimization on your site.
If your content and tags are stuffed with keywords and those keywords are bold, italicized, or underlined (or all three), Google sees this as too much optimization, or trying too hard, and does not like it.
184. Too much optimization on your page.
If the individual page has too much optimization, this is also a serious problem.
185. Ads above the scrolling point.
If you have lots of ads at the top of your page, instead of content, Google will see your page as low quality.
186. Hiding affiliate links, instead of being honest.
If your dealership’s blog ever uses affiliate links to tire sellers, car maintenance products, or other car-related purchases a site visitor could make, and these links are hidden, Google will not approve.
187. Affiliate sites.
Google doesn’t like affiliate sites in general.
188. Computer-generated content.
If you used a computer to generate your content, Google can tell, and it will not like it.
189. Attempts to game the system.
In short, any attempts to game the system will not be looked kindly upon.
190. IP address has been flagged for spam.
If the IP address of your server has been flagged for spam for another website it hosts, your dealership’s website will be affected.
191. Stuffing your meta tags.
Because site visitors can’t see meta tags, man people think they can stuff them full of nonsensical keywords. Google doesn’t approve of this practice.
192. Sudden influx of links.
If a huge number of links suddenly appear to your website, Google sees this as artificial.
193. Penalized by Penguin.
If your website has a Penguin Penalty, it will have a lower ranking.
194. Your link profile is full of low-quality links.
If your ratio of low-quality links to high-quality links is high, Google will think you are trying to play the algorithm and will punish you.
195. Links on unrelated sites.
If you have lots of links on unrelated sites, Google will see this as low-quality linking and may even give you a Penguin Penalty.
196. You didn’t heed an unnatural link warning.
Google usually sends out a warning about unnatural links before they drop your ranking.
197. Too many links on one IP address.
This usually means that you’ve been building a blog network just to use for linking and Google will drop your ranking if it senses this.
198. Google manually penalizes you.
If you have done something that they do not like, but isn’t yet a part of the algorithm, they can manually drop your ranking.
199. Selling links.
If Google catches you selling link space on your website (or buying them), they can drop your ranking.
200. Reconsideration requests.
Submitting one of these requests if you have been penalized can remove a flag that is running your rating.
STILL HAVE QUESTIONS ABOUT AUTOMOTIVE SEO?
Contact 814 Interactive now for your free consultation! We provide a quick and actionable review of your digital marketing and provide you with a free strategic plan to bring you MORE TRAFFIC, MORE CLIENTS, & MORE PROFIT!!